Why Nutrition Is the Foundation of Muscle Growth
Nutrition tips for building muscle are essential for anyone looking to gain strength and transform their physique. Here are the most important strategies to get you started:
- Eat enough calories – Aim for 300-500 extra calories per day above your maintenance level.
- Prioritize protein – Consume 1.6-2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight daily.
- Fuel with carbohydrates – Include at least 3-5 grams per kilogram to power your workouts.
- Include healthy fats – Get 0.5-1.5 grams per kilogram for hormone production.
- Stay consistent – Spread meals throughout the day and stick to your plan.
- Combine with resistance training – Train each muscle group 2-3 times per week.
- Get adequate sleep – Aim for 7-9 hours nightly for optimal recovery.
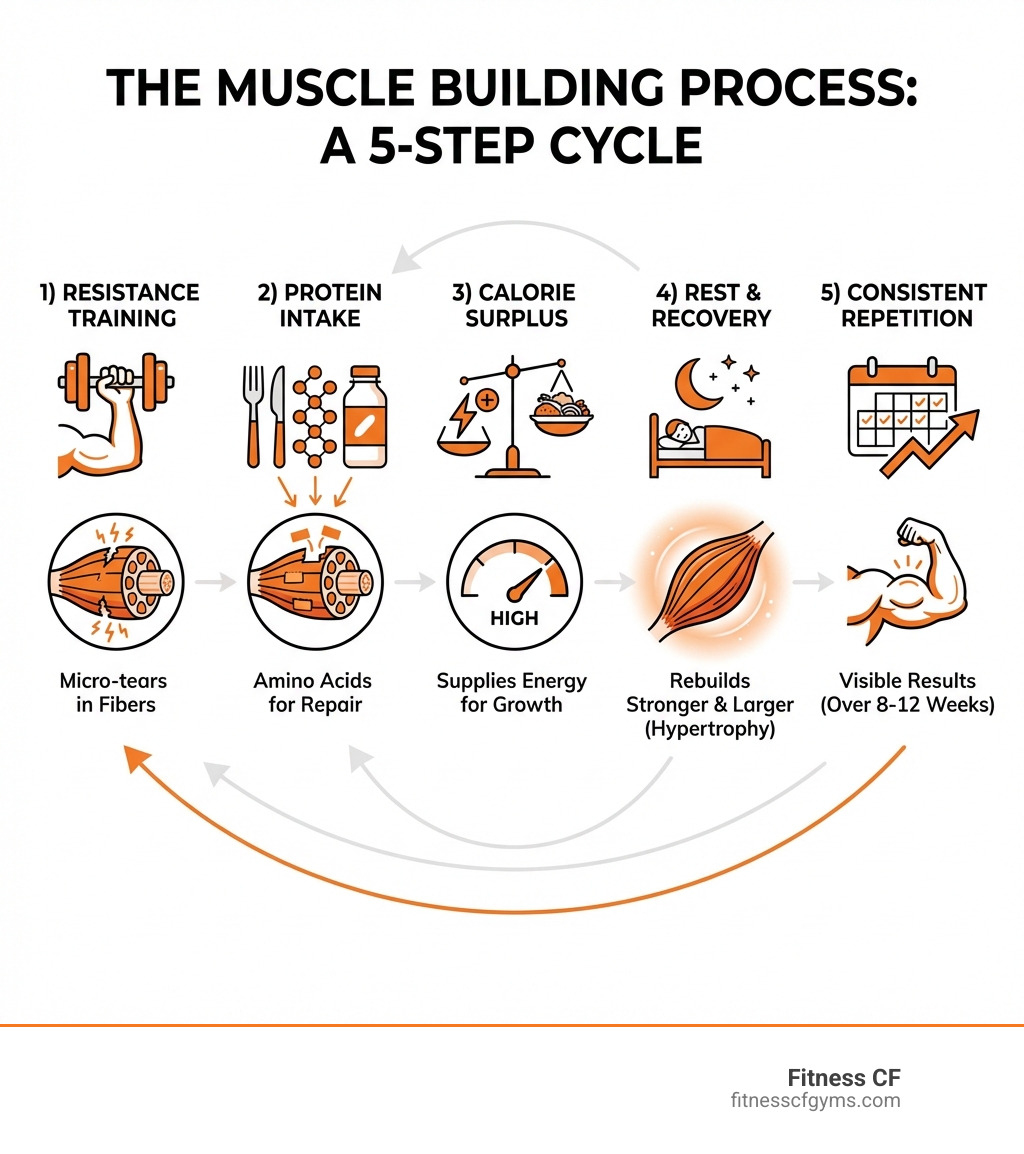
Building muscle isn’t just about lifting weights. Your nutrition is the foundation that determines whether your hard work in the gym translates into real results. After age 30, physically inactive people can lose 3-8% of their lean muscle mass every decade. This age-related muscle loss, called sarcopenia, makes proper nutrition even more critical. The good news is that with the right eating strategy and consistent resistance training, you can build muscle at any age.
The science is clear: muscle growth requires adequate calories for energy, sufficient protein to build tissue, and strategic nutrient timing. Without proper nutrition, even the most intense workout program will fall short. The strategies that follow are based on scientific research and real-world results.
Know your nutrition tips for building muscle terms:
The Building Blocks: Mastering Calories and Macronutrients
To build muscle, our bodies must repair and grow new tissue more efficiently than they break it down. This process, muscle protein synthesis (MPS), is heavily influenced by what we eat. The cornerstones of a muscle-building diet are a caloric surplus and a proper balance of macronutrients (protein, carbohydrates, and fats).

Calculate Your Calorie Needs
To build muscle, we must consume more calories than our body burns, a state known as a caloric surplus. As registered dietitian Erik Bustillo notes, “adequate calories are a priority for gaining muscle.” Without enough energy, our bodies might break down muscle instead of building it.
A good starting point is an additional 300-500 calories above your daily maintenance level. You can estimate maintenance calories by multiplying your body weight in pounds by 16-18. For example, a 150-pound person might target 2700-3200 calories per day for muscle growth. The goal is a gradual weight gain of about 0.25-0.5% of your body weight per week to minimize fat gain. For a deeper dive, you might find this review of macronutrient needs for bodybuilding insightful.
Prioritize Protein for Muscle Repair
Protein provides the essential amino acids needed to repair muscle fibers damaged during exercise. The International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN) recommends 1.4-2.0 grams of protein per kilogram (kg) of body weight daily for active individuals, with some research suggesting up to 2.2 g/kg/day may be beneficial. Leucine is a key amino acid that triggers MPS.
Here are some high-protein foods:
- Chicken breast: Lean and versatile.
- Salmon: Provides protein and healthy omega-3 fats.
- Eggs: Whole eggs are particularly effective for post-exercise muscle protein synthesis.
- Greek yogurt: A convenient, high-protein snack.
- Lentils and Beans: Excellent plant-based protein and fiber sources.
- Tofu and Tempeh: Versatile, complete plant-based proteins.
Total daily protein intake is more important than precise timing. For more details, check out The ISSN’s position on protein and exercise and our information on Protein.
Fuel with Complex Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates fuel the work needed to stimulate muscle growth. They are converted into glycogen and stored in our muscles to power intense workouts. Without enough carbs, performance suffers. After meeting protein and fat needs, the remaining calories should come from carbohydrates, with an intake of at least 3-5 g/kg/day.
Carbs are also crucial for post-workout recovery, as they replenish depleted glycogen stores. Focus on complex carbohydrates for sustained energy.
Some beneficial complex carbohydrates include:
- Oats
- Brown rice
- Quinoa
- Sweet potatoes
- Whole-wheat bread
For tips on post-workout meals, explore our guide on What to Eat After a Workout.
Don’t Fear Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are vital for hormone production, including testosterone, which is essential for muscle growth. Dietary fats should account for 20-35% of total calories, or about 0.5-1.5 g/kg/day. Prioritize monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, including omega-3s.
Sources of healthy fats include:
- Avocados
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, walnuts, chia, flaxseeds)
- Olive oil and canola oil
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
Omega-3s offer numerous health benefits that support your fitness goals. For more information, consult A healthy approach to dietary fats.
Advanced Nutrition Tips for Building Muscle
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore advanced strategies like nutrient timing, body recomposition, and smart supplementation to optimize your results.

The “Anabolic Window”: Fact vs. Fiction
The “anabolic window” refers to a supposed narrow timeframe post-workout for optimal nutrient absorption. While consuming protein and carbs around your workouts is beneficial for recovery, research suggests this window is wider than once thought. Total daily protein intake is more critical for long-term muscle growth than precise timing.
Consistently meeting your daily protein and calorie goals is the priority. However, pre-workout nutrition can boost performance, and post-workout nutrition can kickstart recovery. We recommend distributing protein intake evenly throughout the day, aiming for 0.40-0.55 g/kg per meal across 3-6 meals. For a comprehensive look, read The ISSN’s position on nutrient timing or our guide on The Role of Nutrition in Fitness: What to Eat Before and After a Workout.
Can You Build Muscle and Lose Fat Simultaneously?
Body recomposition, or building muscle while losing fat, is possible. It focuses on improving your body’s ratio of lean muscle to fat, rather than just the number on the scale.
Key strategies for body recomposition include:
- High-protein diet: Aim for 1.5-2.0 g of protein per kg of body weight to preserve muscle during fat loss.
- Moderate calorie deficit: A small deficit of 250-500 calories per day allows for sustainable fat loss without sacrificing muscle.
- Strength training: Resistance training is essential to signal muscle growth and boost metabolism, as supported by research showing its effect on muscle strength and size.
Beginners often see rapid results (“newbie gains”), but for others, it’s a slow, steady process. For more tips, see our article on Nutrition Tips for Building Muscle and Losing Fat.
Nutrition for Aging Muscles
After age 30, we naturally lose muscle mass (sarcopenia), making targeted nutrition and training increasingly important. With the right strategy, you can counteract this and build muscle at any age. Check out these tips on How To Build Muscle Over 50.
For aging muscles, focus on:
- Increased protein needs: Older adults may need slightly more protein to overcome “anabolic resistance.”
- Leucine-rich foods: Leucine remains a key amino acid for stimulating muscle protein synthesis.
- Consistent resistance training: This is the primary signal for muscles to grow and adapt.
- Vitamin D: Adequate levels are important for muscle function.
Building muscle as we age is about maintaining strength and quality of life. Our guide on How to Build Muscle Mass Simply and Guaranteed can provide further insights.
Smart Supplementation: What’s Worth It?
While whole foods should be your priority, a few scientifically-backed supplements can help. Use them to fill gaps, not as a replacement for a solid diet.
Consider these evidence-based supplements:
- Creatine Monohydrate: One of the most effective supplements for increasing strength and muscle mass (3-5 grams/day).
- Protein Powders (Whey, Casein, Plant-Based): A convenient way to meet daily protein goals. Research shows no significant difference between soy and animal protein for muscle gains.
- Caffeine: Can improve performance and reduce perceived effort during workouts (5-6 mg/kg of body weight pre-workout).
- Beta-Alanine: Delays fatigue during high-intensity sets lasting 60-240 seconds (3-5 grams/day).
- Citrulline Malate: May reduce muscle soreness and improve performance (around 8 grams).
Always choose reputable brands that use third-party testing. Operation Supplement Safety for third-party testing is a helpful resource. For more on protein, see The Truth About Protein: How Much Do You Really Need?.
The Holistic Approach: Training, Lifestyle, and Consistency
Building muscle requires a holistic approach that integrates nutrition with effective training, adequate rest, and a consistent mindset.
Key Resistance Training Principles
Nutrition and training are two sides of the same coin. To grow, muscles need a reason to adapt.
Your program should focus on:
- Progressive Overload: Continually challenge your muscles by gradually increasing weight, reps, or sets. This is the most fundamental principle.
- Training Volume: Aim for 10-20 sets per body part per week for optimal growth.
- Frequency: The CDC recommends strength training at least twice a week. Training each muscle group 1-2 times weekly allows for sufficient stimulus and recovery.
- Compound Exercises: Prioritize multi-joint movements like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses to build overall strength and mass.
- Proper Form: Always prioritize correct technique over heavy weight to prevent injury and maximize effectiveness.
These principles induce muscle hypertrophy, the process of increasing muscle fiber size. Understanding what muscle hypertrophy is helps optimize training. For workout structure guidance, see our article on How to Structure Lean Muscle Workouts.
The Overlooked Essentials: Sleep and Stress
What happens outside the gym is just as important. Sleep and stress management are critical for muscle growth.
- Sleep for Recovery: Muscle repair primarily occurs during sleep. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night for optimal recovery and hormone balance. Insufficient sleep can increase cortisol, a stress hormone that promotes muscle breakdown.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress also lifts cortisol, hindering muscle growth. Manage stress through mindfulness, meditation, or hobbies to improve recovery.
For more on how exercise impacts the body, read The Science of Fitness: How Exercise Impacts Your Body.
How to Track Progress Beyond the Scale
The scale can be misleading since muscle is denser than fat. Use multiple metrics to track progress.
Effective tracking methods:
- Progress Photos: Take photos every 4-6 weeks to see visual changes.
- Body Measurements: Use a tape measure to track changes in your arms, chest, waist, and thighs.
- Strength Gains: Lifting heavier or doing more reps are clear indicators of progress.
- How Clothes Fit: A great sign of positive body recomposition.
- Body Fat Percentage: Periodically assess body fat for a more accurate picture of your progress.
Our Build Muscle Lose Fat Workout Plan emphasizes these methods.
Practical tips for maintaining consistency in your nutrition
Consistency is the secret to long-term success.
- Meal Prepping: Prepare meals and snacks in advance to ensure healthy options are always ready.
- Planning Balanced Meals: Create a weekly menu to simplify grocery shopping and reduce decision fatigue. Our guide on balanced meals can help.
- Keeping Healthy Snacks Available: Stock your pantry with protein-rich snacks like Greek yogurt, nuts, and fruit. See our tips for healthy snacks.
- Creating a Routine: Eat every two to four hours to maintain energy and support muscle growth.
- Finding a Supportive Community: A workout buddy or supportive group can help with motivation and accountability.
Consistency over perfection is key. For more advice, refer to our Nutrition Tips: Complete Guide.
Building Muscle Safely: Understanding the Risks
While the journey to build muscle can be incredibly rewarding, approach it safely and realistically. There are potential pitfalls, particularly concerning extreme body fat levels and the use of performance-enhancing substances, that we must be aware of.
The Dangers of Extremely Low Body Fat
For competitive bodybuilders, reaching extremely low body fat levels (typically 5–10% for males and 10–15% for females) is often a goal. However, maintaining these levels can come with significant health risks. Research indicates that extremely low body fat, especially when combined with low calorie intake, can negatively impact our health in several ways:
- Hormonal Disruption: It can lead to imbalances in crucial hormones, affecting metabolism and overall bodily functions.
- Decreased Sleep Quality: Our sleep can suffer, hindering recovery and general well-being.
- Negative Mood Effects: Low body fat levels and restricted eating can lead to irritability and affect our mental health.
- Weakened Immune System: Our body’s ability to fight off illness can be compromised, making us more susceptible to sickness.
These risks highlight the importance of pursuing sustainable body fat levels for general health and fitness, rather than the extreme levels seen in competitive environments. You can learn more about these effects in research on the effects of low body fat in competitors.
Why You Should Avoid Anabolic Steroids
The pursuit of rapid muscle gain can sometimes lead individuals down dangerous paths, such as the use of anabolic steroids. While these substances can dramatically increase muscle mass, they come with severe and often irreversible health consequences.
It’s important to know that anabolic steroids are illegal to possess in the US without a prescription. Beyond their legal status, the health risks are extensive:
- Increased Risk of Heart Disease: Steroids can lift blood pressure and cholesterol, significantly increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Decreased Fertility: They can suppress natural hormone production, leading to reduced sperm count and even infertility in men.
- Mental Health Conditions: Steroid use is linked to mental health issues like depression, severe mood swings, and increased aggression.
Unrealistic expectations fueled by misleading advertising for some supplements can also contribute to body dissatisfaction, potentially leading to the urge to try anabolic steroids. We firmly believe that sustainable, healthy muscle building is achieved through consistent, natural methods. For more detailed information on the severe consequences, refer to the health risks of anabolic steroids.
Frequently Asked Questions about Nutrition for Muscle Building
We often hear many questions about nutrition tips for building muscle. Let’s address some of the most common ones.
How much protein do I need to eat in one meal?
While total daily protein intake is paramount, there’s also a sweet spot for protein per meal. Generally, muscle protein synthesis is maximized with 25-40 grams of high-quality protein per meal. For larger individuals or those performing whole-body resistance exercise, 40 grams or more may be more beneficial than 20 grams. The key is to spread our protein intake throughout the day across 3-6 meals. This consistent supply of amino acids helps optimize muscle repair and growth. Aiming for 25-30 grams of protein in each meal is a practical approach for body recomposition. For more insights, check out The Truth About Protein: How Much Do You Really Need?.
Are plant-based diets effective for building muscle?
Absolutely! A well-planned vegetarian or vegan diet can be highly effective for building muscle. The key is careful planning to ensure we consume a complete amino acid profile, especially focusing on leucine intake. Plant-based protein sources like soy, pea, and rice protein have been shown to be effective. Research, for instance, supports soy protein for muscle development. Studies have even shown no significant difference between supplementing with soy protein versus animal protein on gains in muscle mass and strength in response to resistance exercise. With a diverse range of plant proteins and potentially some supplementation (like pea protein powder), plant-based athletes can achieve impressive muscle gains.
How long does it take to see muscle growth?
Patience is a virtue, especially when it comes to muscle building. While strength gains often come sooner (within a few weeks as our nervous system adapts), visible changes in muscle size typically take 8-12 weeks of consistent training and nutrition. It’s a long-term journey, not an overnight change. Progress is highly individual and depends on several factors, including our genetics, training history (beginners often see faster “newbie gains”), and most importantly, our consistency with both our diet and exercise regimen. Being realistic and celebrating small victories along the way will keep us motivated.
Conclusion: Your Path to Sustainable Muscle Growth
Building muscle is a transformative journey that extends far beyond the gym. It’s a holistic endeavor that demands dedication to smart nutrition tips for building muscle, effective training, and a healthy lifestyle. We’ve explored the crucial role of a caloric surplus, prioritizing protein for repair, fueling with complex carbohydrates for energy, and including healthy fats for hormonal balance. We’ve also digd into advanced strategies like body recomposition, supporting aging muscles, and making smart supplementation choices.
Consistency is our most powerful tool. It’s about making sustainable choices day in and day out, not chasing quick fixes. At Fitness CF, we believe in empowering our members in Central Florida, whether you’re in Orlando, Clermont North, Clermont South, Mount Dora, or St Cloud, to achieve their fitness goals through proven methods.
Your path to sustainable muscle growth is unique, but the principles remain the same. Accept the journey, be patient with yourself, and celebrate every step of progress. If you’re ready to take the next step and need guidance, we’re here to help. Learn more about our personal training programs to guide your fitness journey and open up your full potential.







